Don’t Forget About Biceps
Rotator cuff injuries are a common cause of shoulder pain and dysfunction. It commonly affects athletes, manual laborers, and the general population alike. While the rotator cuff itself—the group of muscles and tendons stabilizing the shoulder joint—often takes center stage in discussions, the role of the biceps tendon in these injuries is equally significant yet frequently overlooked. This blog explores the relationship between the biceps tendon and rotator cuff injuries. It will shed light on diagnosis, treatment, and injury prevention strategies of the biceps tendon.
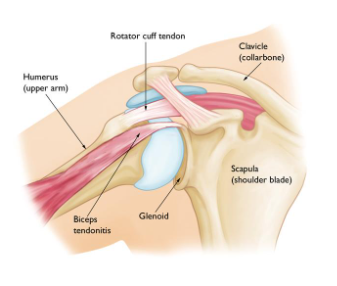
Anatomy and Function of the Biceps Tendon
The biceps muscle has two tendons at the shoulder: the long head and the short head. The long head of the biceps tendon originates from the superior glenoid tubercle of the scapula and travels through the bicipital groove of the humerus. This tendon plays a crucial role in shoulder stability and movement, especially during overhead activities.
The Relationship Between Biceps and Rotator Cuff Injuries
-
Anatomical Proximity:
The biceps tendon and the rotator cuff tendons are anatomically close, sharing the same space in the shoulder joint. This proximity means that injuries to the rotator cuff often involve the biceps tendon as well. -
Mechanism of Injury:
Repetitive overhead activities, trauma, or degenerative changes can lead to injuries. When the rotator cuff is damaged, the biceps tendon can be subjected to increased stress and strain, leading to inflammation or tears. -
Pathophysiology:
Inflammation of the biceps tendon (biceps tendinitis) often accompanies rotator cuff injuries. In some cases, the tendon may partially or completely rupture, exacerbating shoulder pain and dysfunction.
Symptoms of Bicep Tendon Involvement
Patients with biceps tendon involvement in rotator cuff injuries often present with:
- Anterior shoulder pain, particularly during overhead activities.
- Weakness in shoulder movements.
- A popping or catching sensation in the shoulder.
- Tenderness over the bicipital groove.
How is this Diagnosed?
-
Physical examination:
Physical tests such as strength, range of motion, and special tests (ex. Speed’s test and Yergason’s test) can help identify biceps tendon pathology. -
Imaging studies:
Ultrasound and MRI are crucial for visualizing the extent of tendon damage and identifying concurrent rotator cuff injuries.
Treatment Options
-
Conservative management:
Rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications.
Physical therapy focusing on strengthening the shoulder muscles and improving flexibility. -
Medical management:
Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and pain. -
Surgical Intervention:
In cases of severe tendon damage, surgical options such as biceps tenotomy or tenodesis (reattaching the tendon to a different location) may be considered.
Rotator cuff repair may be performed simultaneously to address both issues.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing biceps tendon involvement in rotator cuff injuries involves:
-
Strengthening exercises:
Focus on building shoulder and rotator cuff strength to support joint stability. -
Flexibility and Mobility:
Regular stretching and mobility exercises to maintain a full range of motion. -
Proper Techniques:
Ensuring correct techniques in sports and activities to minimize undue stress on the shoulder tendons. -
Gradual Progression:
Avoiding sudden increases in activity intensity or duration to prevent overuse injuries.
Need more help?
The biceps tendon plays a critical role in shoulder function and is often implicated in rotator cuff injuries. Understanding the relationship between these structures is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. By combining clinical expertise with appropriate diagnostic tools and tailored treatment plans, healthcare professionals can significantly improve outcomes for patients with these complex shoulder injuries. PhysioNow is a leading provider of Physiotherapy Services. Whether it is a sports injury or long term shoulder injury, our therapists can set you on the road to recovery. Book with PhysioNow today for your first assessment and treatment!




Leave a Reply