IASTM, or Instrument-Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization, is a manual therapy technique used by physical therapists, chiropractors, and other healthcare professionals. It is used to diagnose and treat various musculoskeletal conditions. In this blog, we’ll explore what IASTM is, how it works, and the conditions in which it can be beneficial.
What is IASTM?
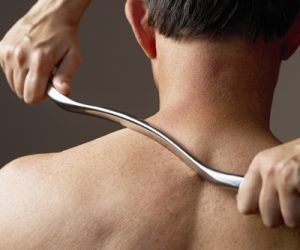
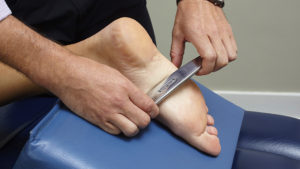
IASTM involves the use of specially designed instruments, like above, often made of stainless steel or plastic, to assess and treat soft tissue abnormalities. These instruments have various shapes and edges that allow the practitioner to detect and treat adhesions, fascial restrictions, and other soft tissue abnormalities. Additionally, IASTM practices have been further refined into methodologies to be followed by clinicians, an example of which is called the Graston Technique.
How does it work?
The process typically involves the following steps:
1. Assessment: Firstly, the practitioner assesses the patient’s musculoskeletal condition. For example, they use the instruments to scan the skin and underlying tissues and identify areas of restricted mobility or dysfunction.
2. Treatment: Secondly, once problem areas are identified, the practitioner applies controlled pressure with the instrument over these areas. As a result of this pressure, it helps to break down adhesions and fascial restrictions, promoting better tissue function and blood flow.
3. Stretching and Range of Motion: Next, after treating the affected areas, the practitioner may incorporate stretching and range of motion exercises to further improve mobility and flexibility.
4. Reassessment: Finally, the practitioner reassesses the patient to determine the effectiveness of the treatment and to make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Conditions IASTM Can Help With:
IASTM can be beneficial for a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions and injuries, including:
1. Soft Tissue Injuries: Firstly, it is effective in treating conditions like muscle strains, ligament sprains, and tendonitis. It breaks down fascial adhesions and promotes tissue healing.
2. Chronic Pain: Secondly, patients with chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia or myofascial pain syndrome. Patients may find relief through IASTM treatments that target trigger points and muscle tightness.
3. Post-Surgical Rehabilitation: Thirdly, this technique can be incorporated into post-surgical rehabilitation programs. It will improve tissue healing, reduce pain, and enhance mobility.
4. Sports Injuries: Additionally, athletes often use this technique to address sports-related injuries like shin splints, tennis elbow, or rotator cuff injuries. Incorporation of this technique can expedite recovery and reduce pain.
5. Joint Dysfunction: Alternatively, this technique can also be used to address joint dysfunction by improving the mobility of surrounding soft tissues. Furthermore, this improvement can positively contribute to joint stability and function.
6. Neck, Hip and Back Pain: In addition, individuals suffering from chronic neck, hip or back pain may benefit from IASTM treatments to alleviate muscle tightness and improve posture.
How can I receive IASTM?
Overall, it’s important to note that IASTM should be administered by trained healthcare professionals who are knowledgeable about the technique. The intensity and duration of treatment can vary depending on the specific condition and the patient’s individual needs.
In conclusion, IASTM is a valuable manual therapy technique used to diagnose and treat various musculoskeletal conditions. It addresses soft tissue abnormalities by breaking down fascial restrictions, improving blood flow, and enhancing tissue mobility. Thus, it makes it a versatile and effective approach for many individuals seeking relief from musculoskeletal pain and dysfunction.
If you’re considering IASTM as a treatment option, consult with a qualified healthcare provider like a physiotherapist to determine if it’s appropriate for your specific condition. Book with PhysioNow today for your first assessment and treatment with a Registered Physiotherapist!





Leave a Reply