De Quervain’s Disease/ Texting thumb.
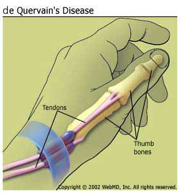
De Quervain’s Disease
De Quervain’s Disease or nowadays known as texting thumb is a painful inflammation of tendons in the thumb that extend to the wrist. The rubbing of the inflamed tendon against the canal it passes through causes pain at the base of the thumb and into the lower arm. It is commonly seen in females over 40 years of age.
Causes of De Quervain’s Disease
1. Simple strain injury to the tendon.
2. Repetitive motion injury. Workers who perform rapid repetitive activities involving pinching, grasping, pulling or pushing are at increased risk. Specific activities including intensive mousing, trackball use, and typing. Other activities including bowling, golf, fly-fishing, piano-playing, sewing, and knitting can also cause De Quervain’s Disease.
3. Frequent causes of De Quervain’s Disease include stresses such as lifting young children into car seats, lifting heavy grocery bags by the loops, and lifting gardening pots .
4. De Quervain’s Disease often occurs during and after pregnancy. Factors may include hormonal changes, fluid retention and more lifting.
5. Rheumatoid arthritis.

De Quervain’s Disease/ Texting Thumb
Onset and Symptoms of De Quervain’s Disease
Onset can be gradual or sudden. Pain is felt along the back of the thumb. There can be Pain directly over the thumb tendons, and pain may travel into the thumb or up the forearm. The bottom of the thumb or the side of the wrist might also be sore or swollen.
It may be hard and painful. Symptoms may get worse when the thumb is moved, particularly when pinching or grasping things. Some people also have swelling and pain on the side of the wrist at the base of the thumb. The back of the thumb and index finger may also feel numb. People might experience a funny sound like a squeak, crackle, snap, or creak when they move the wrist or thumb.
If the condition is not well addressed, the pain can spread up your forearm or down into your thumb.
How is De Quervain’s Disease diagnosed?
De Quervain’s Disease is diagnosed based on history and physical examination. X-rays, or ultrasound may be used to rule out other causes of pain.The Physiotherapist may use special tests to help diagnose De Quervain’s. More information can be found here.
Physiotherapy Treatment
Your Physiotherapist will likely recommend that you wear a specific wrist splint with a thumb spica for 4 to 6 weeks . PhysioNow carries these wrist splints in stock. You’ll also need to stop doing activities that worsen the condition.
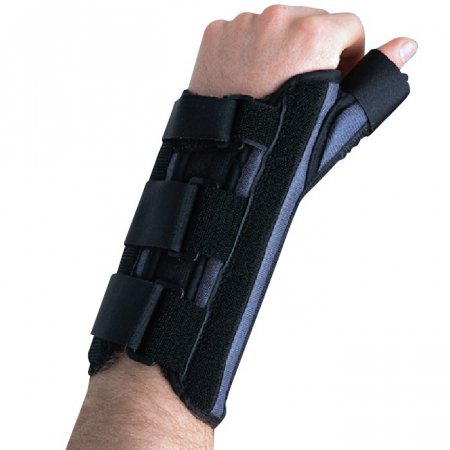
De Quervain’s Disease
The physiotherapist after a thorough assessment could choose different therapy approaches to help with the swelling, pain, and function.
These treatments may include Ultrasound, K-taping, acupuncture, and manual therapy. Other Physiotherapy treatments may include specific exercises focusing on range of motion, strength, and flexibility. These would be given for a safe and effective return back to function.
Recovery times vary depending on your age, general health, and how long you’ve had the symptoms.
If your disease has developed gradually, it’s often tougher to treat. So, it may take you longer to get relief. Your doctor may give you anti-inflammatory medication, or may inject the area with steroids to curb pain and swelling.
In our experience at PhysioNow, more than 99% of people with De Quervain’s Disease get better with Physiotherapy treatment provided. If however, you are one of the outliers, your doctor may recommend surgery. The operation would release the tendon’s tight covering so that the tendon could move smoothly. It’s an outpatient procedure, which means you go home afterward. Your doctor will recommend physiotherapy after surgery which includes an exercise program to strengthen your thumb and wrist.
If you or someone you know suffers from De Quervain’s Disease, please call us today. Our skilled Physiotherapists can Help!



Leave a Reply