A side deviation or curvature in your spine is scoliosis. It could be in your neck, mid back and lower back. It can present in more than one area.
The most common area where it develops is mid-back. Cervical and lumber spine are very common when it comes to two curvatures.
Type of scoliosis:
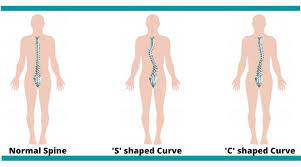
- C-shape: This is most common type, there is only one-sided curve. The most common area for C shape to develop is in the thoracic spine and also lumber spine. In this type, scoliosis side leg could be short compared to non-scoliotic side. Sometimes, there are changes in the scapular level. Scoliotic side scapula will be lower than non-scoliotic side.
- S- shape: In this type, two curvatures are present in the spine. One curvature is the primary scoliosis and the other curvature develops in compensation of the primary curvature. In this type, the scoliotic sided leg is short and the scapular level is higher than the non-scoliotic side. S-shape will bring other complications such as respiratory issues, cardiovascular issues, etc.
Causes of scoliosis:
Usually, the cause of scoliosis is unknown. However, following are a few possible causes mentioned:
- Poor Posture habits: People who have habits of not following ergonomics pattern of posture are at risk. One who has the habit of leaning and sitting mostly on their right or left, are also at risk.
- Carrying heavy stuff on back: People who have to deal with the delivery of heavy packets and lifting heavy objects are at risk.
- Family history: Sometimes, scoliosis runs in family. There are higher chances in these cases.
- Congenital limb length discrepancy: Congenital limb length discrepancy needs immediate correction otherwise; it will lead to scoliosis.
- Neurological disorder: Neurological disorders like cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, Down Syndrome which are progressive diseases have muscular imbalance.
Signs and symptoms:
- Limb length discrepancy
- Visible deviation of spine to one direction
- Uneven shoulder and pelvis height
- In anterior view, one sided rib is popping out.
- Chronic neck and also lower back pain
- Breathing difficulties in severe cases
- Recurrent lung conditions like pneumonia, atelectasis, etc.
- Pain and numbness
- Fatigue due to muscle imbalance
Assessment of scoliosis:
Imaging: X-ray is the gold standard or MRI.
Physiotherapy Assessment: assess in posterior view which means back view with open back.
- Therapist will look for visible prominent border of scapula.
- with bending forward the scapular border will be seen as well as deviation .
- When leaning backward , a visible S shape or C shape will be seen.
Risk factors of scoliosis:
Scoliosis is bony disorientation which is irreversible. The best management is prevention. However, if it not managed well enough , it can lead to many complications.
- Lung disorders: Specially, thoracic spine scoliosis has a chance to affect the respiratory system as it disturbs the alignment of the rib cage. Deep breathing becomes limited or difficult and that is why the lower portion of the lungs get less air. As a result of this, atelectasis develops in some areas of the lung.
- Limb length discrepancy: Lumber scoliosis has a major effect on pelvis alignment. As scoliosis is irreversible, it leads to permanent muscular imbalance. Thus, there is limb length discrepancy.
- Scapular winging: Thoracic scoliosis has drastic effect on scapular orientation. The scapula takes part in shoulder movement. Indirectly, mid back, scapula and the shoulder joint are all affected because of spinal curvature.
- Herniated disc in spine: Lumber spine scoliosis has a higher chance to develop a herniated disc. Therefore, you may develop pain in the lower back and down the leg into the thigh, knee or ankle. Please seek immediate attention in this case.
Management of scoliosis:
Scoliosis is a irreversible bony deformity.
- Posture: Contact your physiotherapist for a better understanding for well maintained posture at work and home. Correction in pelvis alignment will help in preventing it from getting worse.
- Deep breathing exercise: Deep breathing exercise will help in maintaining lung function. Additionally, with breathing exercises, chest mobility exercises will help in maintaining flexibility in the spine and avoid lung conditions like pneumonia, atelectasis, etc.
- Spinal mobility exercises: Contact your physiotherapist for proper exercises. Your Physiotherapist can better assess scoliosis and based on that provide spinal mobility exercises to stop it from getting worse.
- Orthotics: orthotics adjust leg length discrepancy from scoliosis.
- Education: Finally, a physician or physiotherapist can help you to better assess and understand this condition.
Need some help?
Your concerns are best managed by a health care professional. Here at PhysioNow, we have many highly knowledgeable physiotherapists that can assist you with your issue. If you think you may have scoliosis or are diagnosed with it, book with PhysioNow today for your first assessment and treatment!



Leave a Reply